In recent years, the non-destructive testing (NDT) market has seen many exciting advancements with applications ranging from bridges to buildings to aerospace. The introduction of robotics into the NDT space resulted in automating once manual processes to improve efficiency, accuracy, and objectivity. In industrial applications, the evolving robotics market is centered around two remote-controlled technologies: drones and crawlers. Each technology has advantages and disadvantages when it comes to inspection capabilities in the oil & gas, chemical, pulp & paper, and power industries, so there is a lot to consider when deciding which method or technology is the best fit for the inspection scope.
About Industrial Inspection Robots
Drones, or unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV), are remote-controlled devices with the ability to fly, without anyone on board of course! They are commonly used as a means of capturing images or video from high elevations. Today, they are commercially available at reasonably low costs, around $50 for a simple, amateur version. However, industrial inspection drones are much more sophisticated, equipped with high-resolution, infrared cameras, sensors, or other technologies.
Crawler robots do as their name suggests: they inspect equipment such as tanks, boilers, pressure vessels, piping, and more by crawling on the surface. Broadly speaking, crawlers fall into two categories, ones that use magnetic wheels to attach to ferrous material and those that use magnetic tracks. Like drones, crawlers are equipped with high-tech cameras, sensors, and software. But, due to their unique surface interaction, crawlers have more sophisticated ultrasonic testing (UT) data acquisition than drones.
Shared Advantages of Drones and Crawlers
While both technologies function very differently, drones and crawlers offer some of the same general advantages, including but not limited to the following.
Reducing human exposure to potentially hazardous scenarios. Oil & gas, pulp & paper, chemical, and power operations all pose safety risks to personnel. Some are inherent to the specific industry and others arise during maintenance or inspection work. Visual and manual inspections expose personnel to extreme temperatures, high elevations, and confined space entry (CSE). Any time an asset is being accessed using scaffolding, boom lifts, or other equipment, there is a risk of failure, injury, or even death. In most cases, drones and crawlers can eliminate or reduce the risk associated with these situations.
Accomplishing inspections faster than manual NDT. Both robots offer increased efficiency over traditional inspection methods, but, depending on the inspection scope they offer different efficiencies. If the scope only includes a visual inspection, drones can quickly hover around equipment gathering visual data. However, if the scope requires quantitative thickness readings and visual data, state-of-the-art crawlers are 10x faster than traditional inspection methods.
Lessening required on-site personnel. This advantage covers multiple aspects. For starters, drones and crawlers are typically operated by a small team of one to two technicians. And, because of their efficiency, fewer man hours are required to complete the inspection. Additionally, robots are able to reach great heights and can be operated outside the line of sight. Therefore, they reduce the manpower needed to erect scaffolding, operate boom lifts, and hole watch for CSE.
Minimizing downtime. Reducing downtime, and the loss of production and revenue associated with it is paramount for facilities. Both drones and crawlers can successfully perform non-intrusive inspections (NII) from the exterior of the equipment while it’s in-service, and in the case of crawlers, often without reducing the surface temperature. Many companies are exploring NII as a safety, environmental, and financial initiative, and industrial inspection robots are poised to handle the task.
With these similarities, industrial inspection robots have a clear advantage over traditional methods. But, drones and crawlers have their own distinct pros and cons to consider when selecting which technology is best suited for the scope of the inspection.
Pros and Cons of Drones
The pros of industrial drone inspections are:


On the other hand, the cons of drones include:
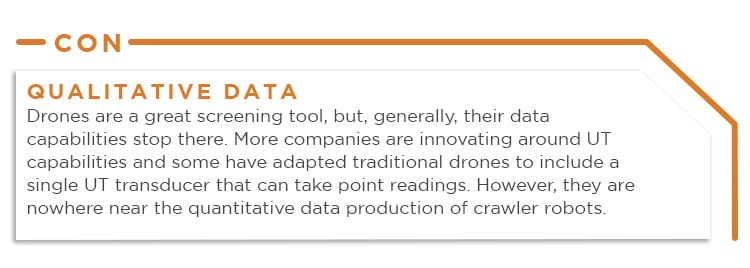


Despite these disadvantages, Inspectioneering explains the significant technological progress in drone inspection technology, particularly when it comes to batteries and motors. The industry can expect to see increased payload capacity in the coming years that will reduce cost and add more value.
Pros and Cons of Crawlers
The pros of industrial crawler inspections are:


Conversely, crawlers also have the following disadvantages:

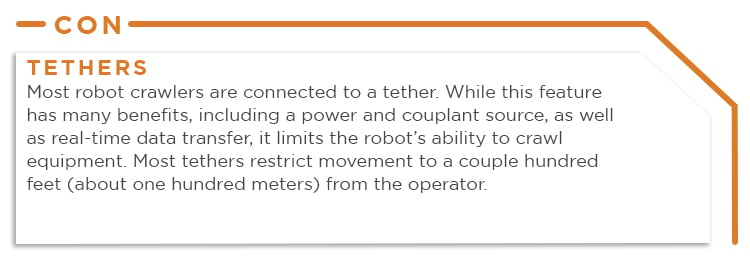
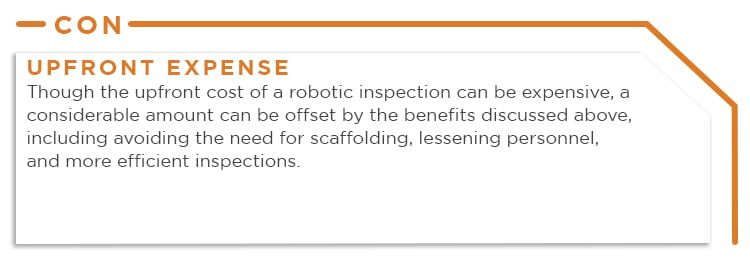
While the above list isn’t exhaustive, both drones and crawlers offer some shared advantages, as well as differing pros and cons. Technology is continually evolving and it won’t be long before many of the disadvantages are eliminated. Best practices recommend considering the inspection scope, maintenance and repair needs, time, budget, and more when choosing the most appropriate technology to achieve site-specific goals.
